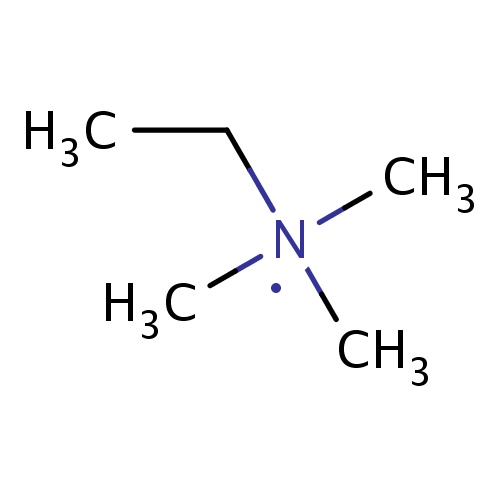
Common name
(trimethyl-λ4-azanyl)ethane
IUPAC name
(trimethyl-λ4-azanyl)ethane
SMILES
C([N](C)(C)C)C
Common name
(trimethyl-λ4-azanyl)ethane
IUPAC name
(trimethyl-λ4-azanyl)ethane
SMILES
C([N](C)(C)C)C
INCHI
InChI=1S/C5H14N/c1-5-6(2,3)4/h5H2,1-4H3
FORMULA
C5H14N

Common name
(trimethyl-λ4-azanyl)ethane
IUPAC name
(trimethyl-λ4-azanyl)ethane
Molecular weight
88.171
clogP
-2.515
clogS
-1.787
Frequency
0.0017
HBond Acceptor
0
HBond Donor
0
Total PolarSurface Area
0
Number of Rings
0
Rotatable Bond
1
| Drug ID | Common name | Structure CAS | Compound class | Therapeutic area |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDBD00290 | Carbachol |

|
Cardiotonic Agents; Analgesics, Non-Narcotic; Parasympathomimetics; Cholinergic Agonists; Miotics; Ophthalmologicals; Sensory Organs; Alimentary Tract and Metabolism; Nervous System; Antiglaucoma Preparations and Miotics; Drugs for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders; Synthetic Anticholinergics, Quaternary Ammonium Compounds; Choline Esters; | Primarily used in the treatment of glaucoma, but is also used during ophthalmic surgery. |
| FDBD00908 | Echothiophate |

|
Cholinesterase Inhibitors; Parasympathomimetics; Miotics; | For use in the treatment of subacute or chronic angle-closure glaucoma after iridectomy or where surgery is refused or contraindicated. |
| FDBD01005 | Bretylium |

|
Antihypertensive Agents; Anti-Arrhythmia Agents; Adrenergic Antagonists; | For use in the prophylaxis and therapy of ventricular fibrillation. Also used in the treatment of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias, such as ventricular tachycardia, that have failed to respond to adequate doses of a first-line antiarrhythmic agent, such as lidocaine. |
| FDBD01089 | Decamethonium |

|
Neuromuscular Depolarizing Agents; | For use as a skeletal muscle relaxant. |
| FDBD01637 | Miltefosine |

|
Antineoplastic Agents; Antineoplastic and Immunomodulating Agents; | For the treatment of mucosal (caused by Leishmania braziliensis), cutaneous (caused by L. braziliensis, L. guyanensis, and L. panamensis), and visceral leishmaniasis (caused by L. donovani). In comparing Leishmania drug susceptibility, it has been found that L. donovani is the most susceptible to miltefosine while L. major is the least susceptible. Off-label use includes treatment of free-living amebae (FLA) infections (unlabeled use; CDC, 2013). |
5 ,
1
| FRAGNAME | PDBID | SIMILIRITY | XSCORE | SMILE | HAC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4bgk_ligand_2_5.mol2 | 4bgk | 1 | -6.10 | [N+](C)(C)(C)CC | 6 |
| 4bhf_ligand_1_0.mol2 | 4bhf | 1 | -6.10 | [N+](C)(C)(C)CC | 6 |
| 1uv6_ligand_2_0.mol2 | 1uv6 | 1 | -6.07 | CC[N+](C)(C)C | 6 |
| 4c5w_ligand_2_1.mol2 | 4c5w | 1 | -6.03 | CC[N+](C)(C)C | 6 |
| 4bgm_ligand_3_6.mol2 | 4bgm | 1 | -6.00 | [N+](C)(C)(CC)C | 6 |
| 3feg_ligand_3_74.mol2 | 3feg | 1 | -5.96 | CC[N+](C)(C)C | 6 |
| 2ha0_ligand_2_0.mol2 | 2ha0 | 1 | -5.89 | C([N+](C)(C)C)C | 6 |
577 ,
58